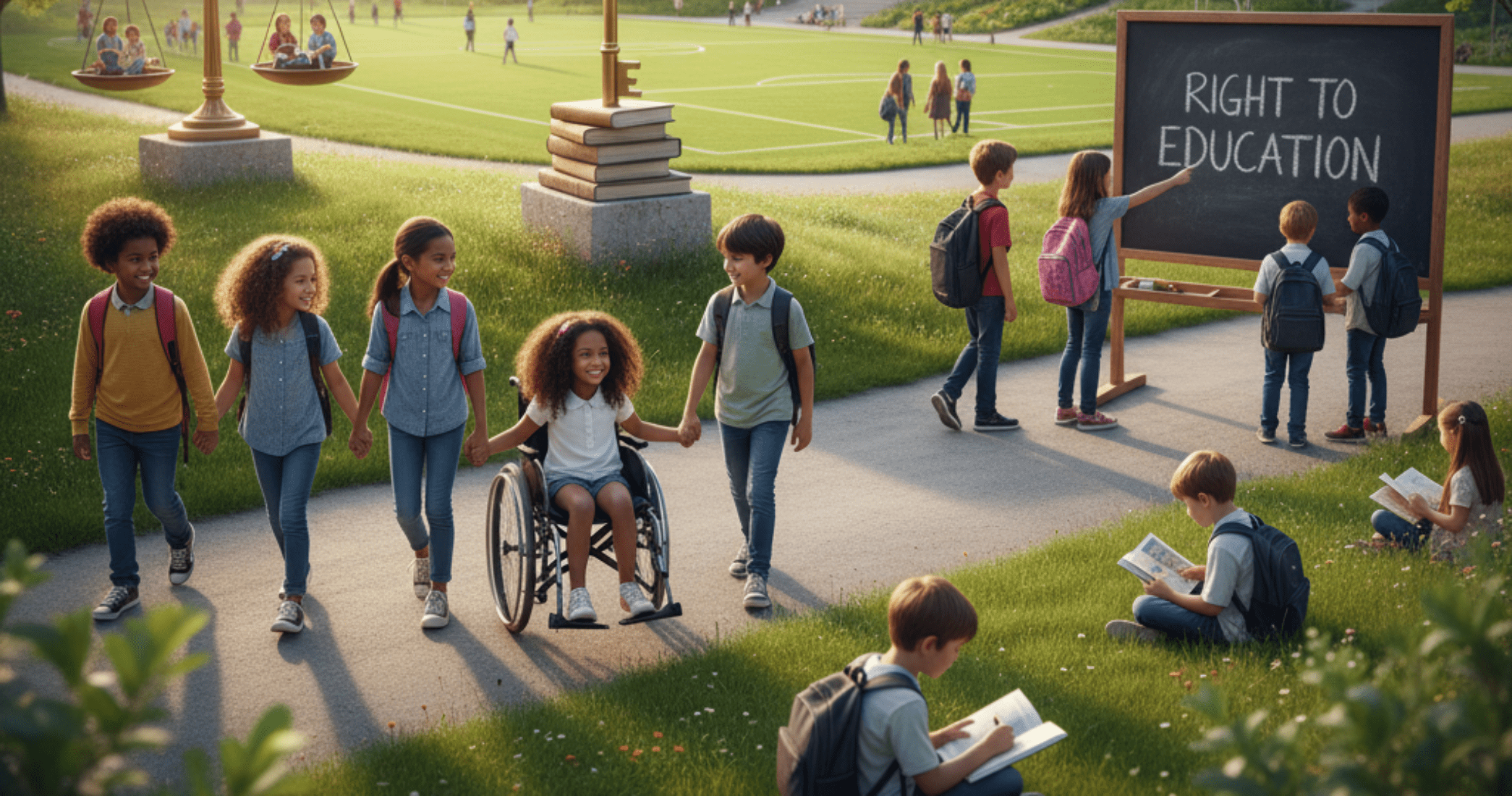Education is more than just classrooms and books. It is the foundation for a progressive, democratic society. Access to quality education in India was once only available to a select few. This changed after the Right to Education Act.
India has taken a major step in ensuring that all children, no matter their background, have the chance to grow and learn.
The Right to Education (RTE ) has changed the way that we look at schooling, equity and responsibility within the education sector. What does this actually mean? Why is it so important? And what are the responsibilities that it places on government, schools and society as a whole. Let’s get started.
Understanding the Right to Education of Indian Children
The right to education guarantees that children aged 6-14 receive a free and compulsory educational experience. In 2009, India became one of few countries where education was made a legal right.
To better understand let’s begin with the RTE full form in education Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Schooling. It is a simple phrase that comes with a great responsibility: providing an education inclusive for all children, especially those from marginalized groups.
The Right to Education Act also mandates that no child be denied admission to school on the basis of caste, religion, gender, or economic status. Inclusion is the key to a more equal society.
Why Education is Important
Education is more than just literacy, it’s empowerment. Lack of education can prevent children from achieving financial independence, employment and making informed decisions. The Right to Education seeks to close this gap through equal opportunities.
RTE is essential for many reasons.
- Bridging Inequality: This reduces social inequality by providing equal learning opportunities to all children, rich or not.
- Economic empowerment : A well-educated population contributes to the growth and development of a nation.
- Social inclusion Education promotes tolerance, inclusivity and equality.
- Foundation of rights awareness : Children are taught their rights and responsibilities at a very young age.
The Right to Education Act, which focuses on access, has opened the door for millions of kids to dream without boundaries.
Objectives Of RTE Act
The objectives of RTE Act 2009 go far beyond opening the school gates. Its vision is to create a solid educational foundation, while also ensuring quality and inclusivity. Some of the major objectives include:
- All children between 6 and 14 years old are entitled to free education.
- Eliminating discrimination from schools and classrooms
- Assuring minimum infrastructure, such as safe classrooms and drinking water.
- To ensure that students receive individualized attention, maintain the ratio of pupils to teachers.
- Promote child-centric learning rather than rote memorization.
- Ensure quality education by ensuring that teachers are trained.
These objectives emphasize that the right to education does not just concern access, but also quality and equity.
Responsibilities under the Right to Education
It is not enough to pass a law; it must be implemented effectively. The Right to Education Act assigns responsibility to multiple stakeholders.
1. The role of the government
It is the state’s primary responsibility to make sure that schools are properly equipped, have well-trained teachers, and are funded to operate effectively.
2. The role of schools
Private schools must reserve 25% of their seats for children who come from the economically weaker sections. The private schools must also avoid screening tests and capitation fees.
3. Parents’ role
It is the parents’ responsibility to enroll and encourage their children’s regular attendance. Many parents from rural and poor urban communities are unaware of their children’s right to education.
4. The Role of Society
Civil society platforms and organizations like vidyalay.org often support awareness campaigns and educational initiatives that complement government efforts.
The Act makes education a collective effort by dividing responsibilities.
Challenges to Implementation
The Right to Education has a transformative effect, but it is not always easy to implement. Some schools still lack proper infrastructure. Teacher shortages, insufficient monitoring and dropouts are still pressing concerns.
In addition, the RTE full form in education is not widely known in India. It is equally important to bridge this information gap as it is to build classrooms.
The Right to Education: Benefits
Despite its challenges, Right to Education Act delivered significant benefits. Millions of previously excluded children are now in school. The social acceptance of equal educational opportunities has increased.
Some of the main benefits include:
- Increased enrollment for girls and children from underprivileged groups.
- An increase in literacy rates across all states
- Focus on holistic and inclusive development.
- Parents need to be more aware of their rights as parents.
Implementing the objectives of RTE Act 2009 effectively will result in a society that is more empowered and equitably distributed.
Strengthening RTE
The Right to Education has been a milestone, but must evolve to meet changing needs. The next steps are to improve teacher training, update curricula and integrate technology into classrooms.
vidyalay.org plays an important role in spreading awareness and providing educational materials. India can continue to benefit from the Right to Education Act by collaborating with government, NGOs and digital platforms.
Final Thoughts
The Right to Education Act does not only represent a law, but a promise. The Right to Education Act is a promise that all children in India will have equal access to education, growth, and knowledge.
Understanding the RTE full form in education and the objectives of RTE Act, 2009 as well as the challenges that it assigns will help us to appreciate the importance of education for national progress.
India’s future depends on our ability to uphold this right. It is not only the responsibility of the government to ensure quality education for everyone, but also that of society collectively. When implemented in true spirit, Right to Education has the potential to transform the lives of individuals and the future of a nation.
FAQs
1. What is the Right to Education Act?
The Right to Education Act in India guarantees free and mandatory education to children aged between 6-14. This act promotes inclusivity, and eliminates any discrimination based on caste, gender, or economic status.
2. What is the right to an education for children?
By providing equal learning opportunities, the Right to Education empowers all children, while also promoting social inclusion and encouraging an awareness of rights and obligations. Education is the basis for personal growth and nation advancement.
3. What does RTE mean in education?
The RTE in education is also known as the “Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education.” It is a legal requirement to provide quality education to all children, especially those who are from marginalized groups.
4 . What are the objectives of RTE Act?
Objectives of RTE act 2009 is to provide free education to children, eliminate all discrimination, ensure a minimum infrastructure, maintain good teacher-student relations, and promote learning centered on children.